ANEMIA
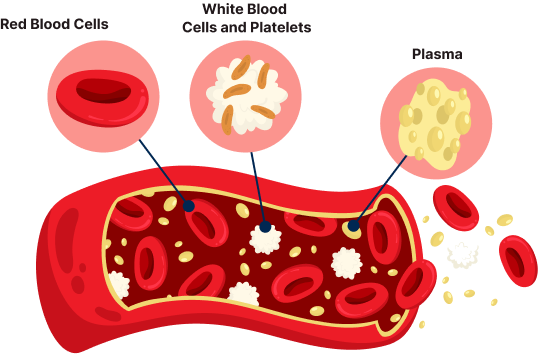
Anemia is a significant public health challenge in India. It has devastating effects on health, physical and mental productivity affecting the quality of life. The prevalence of anaemia among six groups as per the National Family Health Survey 5 (2019-21), is 25.0 % in men (15-49 years) and 57.0 % in women (15-49 years). 31.1 % in adolescent boys (15-19 yrs), 59.1 % in adolescent girls,52.2 % in pregnant women (15-49 years) and 67.1 % in children (6-59 months). Severe iron deficiency anemia may require blood transfusion. Blood transfusion can be a key part of treatment for people with anemia when necessary.