CANCER
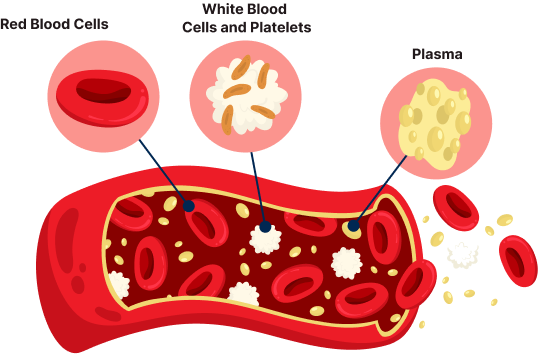
The estimated number of incident cases of cancer in India for the year 2022 was found to be 14,61,427 (crude rate:100.4 per 100,000). In India, one in nine people are likely to develop cancer in his/her lifetime. Lung and breast cancers were the leading sites of cancer in males and females, respectively. Among the childhood (0-14 yr) cancers, lymphoid leukaemia (boys: 29.2% and girls: 24.2%) was the leading site. The incidence of cancer cases is estimated to increase by 12.8 per cent in 2025 as compared to 2020. India registered about 12 lakh new cancer cases and 9.3 lakh deaths in 2019, becoming the second highest contributor to the disease burden in Asia for that year, according to a new study published in The Lancet Regional Health Southeast Asia journal. Apart from tobacco, alcohol, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and environmental factors also contribute to the increase in cancers. Cancer patients often require platelets donation. Platelets are tiny cells in blood that form clots and stop bleeding.