MAJOR TRAUMA
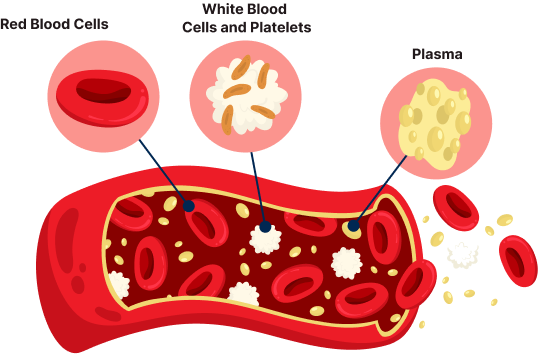
Trauma refers to "any injury caused to the body". The injury may be caused due to any reasons like road accidents, fires, burns, falls, acts of violence. Road Traffic Accidents are the leading cause of trauma in India. A total number of 4,61,312 road accidents have been reported by Police Departments of States and Union Territories (UTs) in the country during the year 2022, claiming 1,68,491 lives and causing injuries to 4,43,366 persons. According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), about 4,13,457 people died in road accidents in India in 2015. These all cases require blood transfusion to stop blood loss and improve clotting parameters.