CHICKENPOX
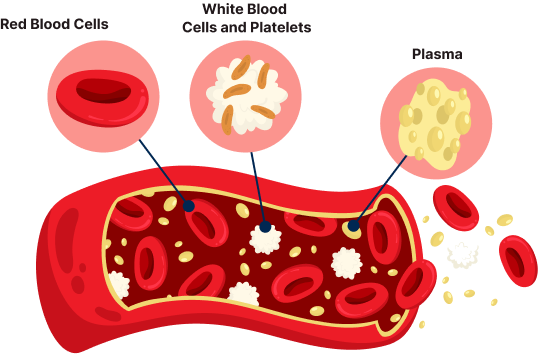
Varicella (chickenpox) is a contagious disease which is caused by varicella zoster virus (VZV) . It is rarely fatal, with only around 1 death per 1,00,000 cases among children agen 1-14 years; 6 per 1,00,000 cases in the 15-19 age group and 21 per 1,00,000 cases in adults. Between Jan 2015 and May 2021, 1269 chickenpox outbreaks (27,257 cases) have been recorded. Thirty-one deaths have been confirmed, with most occurring in Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. Nineteen states did not report any deaths. Among infants less than 1 year old who get the disease, about 1 in 250,000 die. For older children, about 1 in 100,000 die. If a woman gets chickenpox just before or after giving birth, her baby can get very sick. About 1 child in 500 who gets chickenpox is hospitalized. plasma can provide valuable antibodies (blood proteins your body makes to fight infections) for people at risk of chicken pox.